Comprehensive Disaster Management 2
From the previous post, I mentioned about the 6 main components of the conceptual framework of disaster. In this post, the actions that are derived from the main components like what is their definition, function and description will be discussed and I welcome anyone who would want to post any comment or suggestion on my post. Thank you.
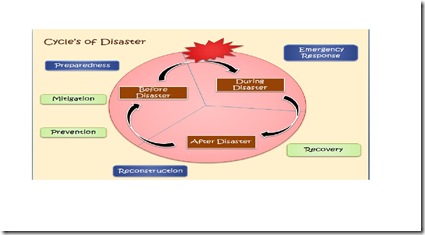
In disaster management, there are 3 phases that forms the framework, which is the pre-disaster phase, during disaster and post-disaster phase. And in these phases the actions derived from the 6 main components of the framework will play their function in disaster managing. The actions are prevention, preparedness, mitigation, resilience, response and recovery.
In prevention, we try to avoid or minimize the hazard. For example, we can do an evacuation. Otherwise, we could also try to prevent the hazard from turning into a disaster by doing selective preventive measures that are useful and effective.
For preparedness, it is a continuous cycle of planning, organizing, training, equipping, exercising, evaluating, improvement activities, and increasing capabilities to prevent, protect against, respond, recover, and mitigate effects of disasters. The actions are preparing a good communication system, preparing the response team, preparing shelter or evacuation plan, stockpiling supplies, trained volunteers (Red Cross, MERCY) and lastly give warnings to the society about the condition of the hazard. In preparedness, casualty prediction is required to anticipate the worst come to worst outcome of the hazard.
As for mitigation, it is defined as an action to lessen or reduce the force or impact of the hazard. The principles of mitigation are to prevent hazard to turn into disaster, reduce the effect of disaster when it occur, and focus on long term measures in reducing or eliminating risk. Mitigation is classified into structural and non-structural measures. Structural mitigation is an engineering measure that deals with the resistance and resilience of the infrastructures, houses, and facilities in reducing the impact of disaster. To increase the ability to face the disaster, non-structural mitigation deals with the awareness of the community, policies from the government and warning system to the community.
In response, there is the mobilization of emergency services and the first responders are to set up an incident command system to coordinate and communicate with other responders. There are many parties that played a role in this action, which are firefighters, police, ambulance, rapid response team, search & rescue team as well as the military soldiers. When this response is conducted as military operation, it is call a disaster relief operation. Vast majority of individuals will die within 72 hours of impact therefore it is of most importance that the victims are to be found within that stated time.
In recovery, there are two sub-actions which are the rehabilitation and the reconstruction. Disaster recovery is the process, policies and procedures related to preparing for recovery or continuation of technology infrastructure critical to an organization after a natural or human induced disaster. Rehabilitation focuses on the improvement and restoration of all aspects of public services and the normalization or the progression of daily life of the affected people. In reconstruction, the redevelopment or development of all infrastructures and facilities are being done to make sure the community affected can regain their daily routine as soon as possible. The recovery process is important so that the community can function properly in order to progress economically, socially, and culturally.
References:
Lecture Notes Block 4.2 (Conceptual Framework of Disaster and Disaster Management, Logistic Management Support, and Preparedness, Response, and Recovery)
A Comprehensive Conceptual Model for Disaster Management
Sohail Asghar, Damminda Alahakoon and Leonid Churilov
Clayton School of Information Technology, Monash University, Australia


No comments:
Post a Comment